Credit: NOAA
Specifications
Contact Info
Honolulu, HI
United States
About the ship
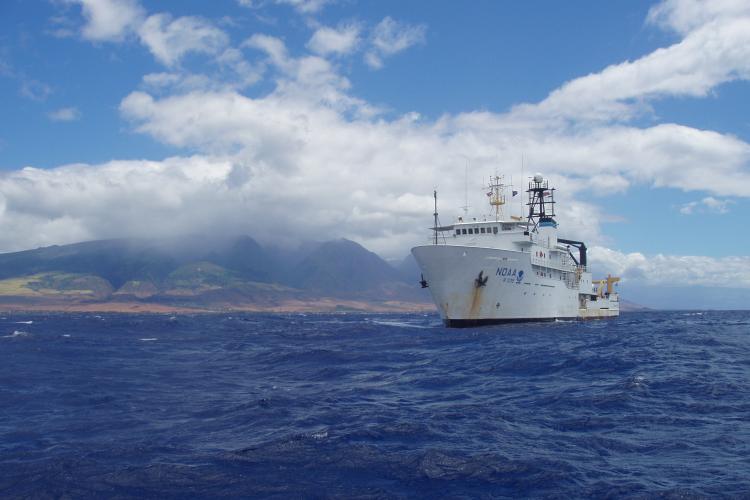
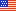
NOAA Ship Oscar Elton Sette was built by VT Halter Marine, Inc. in Moss Point, Mississippi. The ship was commissioned on January 23, 2003 and is homeported in Honolulu, Hawaii. Oscar Elton Sette conducts fisheries assessments, physical and chemical oceanography research, marine mammal surveys, and marine debris surveys. The ship operates throughout the central and western Pacific Ocean.
A T-AGOS class vessel, Oscar Elton Sette was originally built for the U.S. Navy’s Military Sealift Command under the name U.S. Naval Ship Adventurous from 1988 to 1992. In 1992, the 224-ft. ship was transferred to NOAA where it was converted into a research ship. Eventually, Oscar Elton Sette replaced the 39-year-old NOAA Ship Townsend Cromwell in 2003. Because the ship is acoustically quieted, it is particularly well suited to conduct fisheries research and marine mammal surveys.
When conducting fisheries surveys, the ship uses bottom trawls, longlines, and fish traps to collect fish and crustacean specimens--plankton nets and surface and mid-water larval nets are used to collect plankton, fish larvae, and eggs.
Oscar Elton Sette is equipped with six small outboard driven boats for rescue, research, and operations. The ship has wet, dry, hydro-chemistry and computer laboratories. The ship’s on-deck equipment includes two deep-ocean winches, two j-frames, one A-frame, a net reel, and deep-sea trawl winches.
The ship is equipped to handle four divers, who are particularly needed for coral reef health assessments. Ample deck space enables Oscar Elton Sette to carry a recompression chamber as an added safety margin for dive-intensive missions in remote regions.
The ship is named after Oscar Elton Sette who served as the first director of the Honolulu Laboratory at U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (now the NOAA National Marine Fisheries Service’s Pacific Islands Fisheries Science Center), from 1949 to 1955.